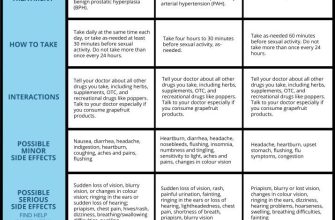
Experiencing difficulty ejaculating while using Cialis? This isn’t uncommon. Several factors can contribute to this, and addressing them often leads to improvement. Let’s explore some possibilities and actionable steps.
Firstly, consider the dosage. A higher dose might increase the likelihood of this side effect. Consulting your doctor about adjusting your Cialis prescription is crucial. They can help determine if a lower dose is suitable for you, potentially resolving the issue without compromising the medication’s effectiveness for its intended purpose.
Secondly, underlying medical conditions can play a significant role. Nerve damage, hormonal imbalances, and certain medications can all interfere with ejaculation. Open communication with your physician is key. A thorough examination can identify any underlying health problems contributing to the issue and suggest appropriate treatments.
Thirdly, lifestyle factors warrant attention. Stress, anxiety, and even alcohol consumption can impact sexual function. Implementing stress-reducing techniques, such as regular exercise or mindfulness practices, may prove beneficial. Limiting alcohol intake can also positively affect your sexual health.
Finally, remember that Cialis isn’t the sole culprit. Other medications you’re taking might interact negatively, affecting ejaculation. Provide your doctor with a complete list of all your prescriptions and over-the-counter medications for a comprehensive assessment. A collaborative approach to managing your medications might be necessary.
Remember: This information is for educational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor before making any changes to your medication or treatment plan.
- No Ejaculation with Cialis: Understanding the Potential Side Effect
- Factors Influencing the Risk
- What to Do if You Experience This Side Effect
- Alternative Treatments
- Understanding the Mechanism of Cialis and Its Impact on Ejaculation
- Rare Side Effects
- Individual Variation and Consultations
- Frequency and Severity of Anorgasmia with Cialis: Statistics and Prevalence
- Studies and Reported Rates
- Factors Influencing Anorgasmia
- Recommendations
- Further Research
- Identifying Risk Factors for Cialis-Induced Anorgasmia
- Differentiating Cialis-Related Anorgasmia from Other Causes of Erectile Dysfunction
- Managing Cialis-Induced Anorgasmia: Lifestyle Changes and Medical Interventions
- Lifestyle Adjustments
- Medical Approaches
- Seeking Professional Help
- When to Consult a Doctor: Seeking Professional Help for Persistent Anorgasmia
- Identifying Potential Underlying Causes
- Diagnostic Tests and Assessments
- Treatment Options and Next Steps
- When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
- Alternative Treatments and Medications: Exploring Options for Patients
- Lifestyle Adjustments
- Alternative Therapies
No Ejaculation with Cialis: Understanding the Potential Side Effect
Cialis can sometimes cause delayed or absent ejaculation. This side effect, known as anorgasmia or anejaculation, isn’t common but warrants understanding. It’s usually temporary and resolves once you stop taking the medication.
Factors Influencing the Risk
Several factors might increase the likelihood of experiencing this side effect. These include higher Cialis dosages, pre-existing conditions affecting sexual function, and the use of other medications, particularly those affecting the nervous system. Consult your doctor to discuss potential interactions.
What to Do if You Experience This Side Effect
If you experience difficulty ejaculating while on Cialis, don’t hesitate to contact your doctor. They can assess your situation, explore alternative treatment options, or adjust your dosage. They may also recommend further investigations to rule out other underlying medical conditions. Open communication with your doctor is key.
Alternative Treatments
Your doctor may suggest alternative erectile dysfunction treatments if Cialis continues to cause this side effect. These could include different medications, lifestyle changes, or even counseling.
Understanding the Mechanism of Cialis and Its Impact on Ejaculation
Cialis, or tadalafil, primarily works by inhibiting phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5), an enzyme that breaks down cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP). Increased cGMP levels relax blood vessels in the penis, facilitating improved blood flow and enabling erections. This mechanism focuses primarily on vascular function; it doesn’t directly affect the neural pathways responsible for ejaculation.
Rare Side Effects
While Cialis doesn’t typically impact ejaculation, some men report delayed ejaculation or a decrease in ejaculate volume as a rare side effect. These effects are usually mild and temporary. The exact mechanism underlying these rare occurrences isn’t fully understood, but potential contributing factors might include subtle interactions with other neurotransmitters or hormonal pathways.
Individual Variation and Consultations
Individual responses to Cialis vary widely. Factors such as age, overall health, and other medications can influence how the drug affects each person. If you experience changes in your ejaculation after starting Cialis, consult your doctor. They can assess your situation and determine if the side effect warrants further investigation or adjustment to your treatment plan.
Frequency and Severity of Anorgasmia with Cialis: Statistics and Prevalence
Reports of anorgasmia (inability to achieve orgasm) with Cialis vary widely. Precise figures are difficult to obtain due to underreporting and inconsistent study methodologies. However, available data suggests a relatively low, but not insignificant, incidence rate.
Studies and Reported Rates
- Some clinical trials show anorgasmia rates ranging from 1% to 5% among men using Cialis. These studies often focus on specific populations and may not represent the broader user base.
- Post-marketing surveillance data, which includes reports from doctors and patients, frequently show higher rates, though these data are not always rigorously controlled for confounding factors such as age, overall health, and other medications.
- Individual experiences differ significantly. Some men report no change in orgasmic function, while others experience a noticeable decrease in orgasmic intensity or complete anorgasmia.
The severity of anorgasmia also varies greatly. It may manifest as difficulty achieving orgasm, reduced intensity of orgasm, or a complete absence of orgasm. These variations make it challenging to establish a clear, single prevalence statistic.
Factors Influencing Anorgasmia
- Dosage: Higher doses of Cialis may be associated with a slightly increased risk of anorgasmia.
- Underlying Health Conditions: Pre-existing conditions affecting neurological or vascular function can increase the likelihood of experiencing difficulties with orgasm.
- Other Medications: Interaction with other medications can affect the incidence of anorgasmia.
- Individual Variability: Genetic predisposition and individual sensitivity to Cialis play a significant role.
Recommendations
If you experience anorgasmia while using Cialis, consult your doctor. They can assess your individual situation, consider potential underlying causes, and adjust your treatment plan accordingly. This might include adjusting the dosage, switching to a different medication, or addressing any underlying health issues contributing to the problem. Open communication with your physician is crucial for effective management.
Further Research
Further large-scale, well-designed studies are needed to provide a more precise understanding of the frequency and severity of anorgasmia associated with Cialis use. These studies should incorporate diverse populations and account for various confounding factors to obtain a clearer picture.
Identifying Risk Factors for Cialis-Induced Anorgasmia
Certain medical conditions increase the likelihood of experiencing anorgasmia while using Cialis. Pre-existing neurological disorders, such as multiple sclerosis or Parkinson’s disease, can interfere with nerve signals necessary for orgasm. Diabetes significantly impacts nerve function, potentially contributing to this side effect.
Mental health plays a crucial role. Anxiety and depression can disrupt sexual function, making achieving orgasm more difficult. Similarly, pre-existing performance anxiety might exacerbate the issue.
Specific medications interact negatively with Cialis. Some antidepressants, particularly selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), are known to cause delayed or absent ejaculation. Combining Cialis with these drugs heightens this risk.
Age is another factor; older men may experience a higher incidence of Cialis-induced anorgasmia due to natural age-related changes in the nervous and vascular systems.
Finally, the dosage of Cialis is relevant. Higher doses may increase the chance of experiencing this side effect. Always discuss dosage with your doctor.
Differentiating Cialis-Related Anorgasmia from Other Causes of Erectile Dysfunction
Consult your doctor. They can accurately diagnose the root cause of your erectile dysfunction (ED) and anorgasmia. Self-diagnosis is unreliable and potentially harmful.
Here’s a breakdown of how your doctor might approach this:
- Thorough Medical History: Your doctor will review your medical history, including current medications (beyond Cialis), past illnesses, and surgeries. They’ll ask about the onset and duration of your symptoms.
- Physical Examination: A physical exam will assess your overall health and neurological function, potentially including a neurological exam to check for nerve damage. This is important for ruling out other conditions.
- Blood Tests: These could check hormone levels (testosterone, prolactin), blood sugar, and cholesterol–factors often involved in ED and related issues.
- Psychological Evaluation: Anxiety, depression, and stress significantly affect sexual function. Your doctor may refer you to a therapist or counselor to address psychological contributions.
Differentiating Cialis-related anorgasmia from other causes relies on several key distinctions:
- Timing: Did anorgasmia begin after starting Cialis? This strongly suggests a medication-related issue.
- Other Symptoms: Cialis-induced anorgasmia typically doesn’t involve other significant ED symptoms, like the inability to achieve an erection. Other causes of ED often involve multiple problems.
- Response to Dosage Adjustment: Your doctor might suggest adjusting your Cialis dosage to see if symptom improvement occurs. This helps determine if Cialis is the main contributor.
- Response to Alternative Treatments: If Cialis adjustment doesn’t help, exploring other ED treatments can reveal whether the problem stems from Cialis specifically or an underlying condition.
Remember, many factors can contribute to ED and anorgasmia. A professional medical evaluation is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Managing Cialis-Induced Anorgasmia: Lifestyle Changes and Medical Interventions
Reduce alcohol consumption. Excessive alcohol intake can significantly impair sexual function, exacerbating anorgasmia. Aim for moderation or abstinence, especially before sexual activity. Similarly, limit caffeine intake, as it can also negatively affect sexual response.
Prioritize sleep. Adequate sleep is crucial for overall well-being and hormonal balance, both impacting sexual health. Aim for 7-8 hours of quality sleep per night. Consider establishing a regular sleep schedule to improve sleep quality.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Manage stress levels. Stress profoundly impacts sexual function. Incorporate stress-reducing techniques like meditation, yoga, or regular exercise into your routine. Consider professional counseling if stress is overwhelming.
Optimize your diet. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins supports overall health and can indirectly improve sexual function. Consult a nutritionist for personalized dietary advice.
Medical Approaches
Discuss alternative medications. Your doctor might suggest adjusting your Cialis dosage or switching to a different medication, such as tadalafil, to manage erectile dysfunction while minimizing anorgasmia. Other medications may also be considered depending on the underlying cause.
Consider psychotherapy. A therapist specializing in sexual health can provide guidance and strategies for overcoming performance anxiety and improving communication with your partner, factors that can contribute to anorgasmia.
Seeking Professional Help
Consult your doctor. Open communication with your physician is essential. They can conduct a thorough assessment, rule out underlying medical conditions, and recommend appropriate treatment options. Don’t hesitate to discuss any concerns you have openly and honestly.
When to Consult a Doctor: Seeking Professional Help for Persistent Anorgasmia
If you experience persistent inability to achieve orgasm despite adequate sexual stimulation for three months or more, schedule an appointment with your doctor. This timeframe helps distinguish temporary issues from chronic anorgasmia.
Identifying Potential Underlying Causes
Your doctor will conduct a thorough review of your medical history and current medications. They will discuss your lifestyle factors, including stress levels and sleep quality, as these can significantly impact sexual function. Openly discussing your sexual history and any relationship concerns is also crucial.
Diagnostic Tests and Assessments
Depending on your symptoms and medical history, your doctor may suggest a physical exam to rule out medical conditions. Blood tests may be used to check hormone levels, while psychological assessments can help identify underlying anxiety or depression. Neurological examination may also be included.
Treatment Options and Next Steps
Treatment for anorgasmia is tailored to the underlying cause. Options range from medication adjustments to therapy focusing on cognitive behavioral techniques or addressing relationship issues. Hormone replacement therapy may be considered in cases of hormonal imbalances. Your doctor will work with you to develop a personalized treatment plan.
| Symptom | Possible Cause | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Inability to reach orgasm despite sufficient stimulation | Hormonal imbalance, medication side effects, psychological factors, neurological conditions | Consult a doctor for evaluation |
| Decreased libido alongside anorgasmia | Depression, anxiety, stress, relationship problems | Seek therapy and discuss potential medication adjustments with your doctor |
| Sudden onset of anorgasmia | New medication, recent stressful event, underlying medical condition | Immediately contact your doctor |
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
If you experience sudden changes in sexual function, or if anorgasmia is accompanied by other concerning symptoms like pain during intercourse or changes in urination, seek medical attention immediately. Prompt diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications.
Alternative Treatments and Medications: Exploring Options for Patients
Consider talking to your doctor about alternative treatments. Phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5) inhibitors like tadalafil (Cialis) can sometimes cause ejaculation difficulties. However, other PDE5 inhibitors, such as sildenafil (Viagra) or vardenafil (Levitra), might be better tolerated. Your physician can assess your individual needs and suggest the most appropriate option.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Certain lifestyle changes can positively influence erectile function and ejaculation. Regular exercise improves blood flow throughout the body, including the genitals. Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the risk of several health conditions that can impact sexual performance. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains provides the nutrients needed for optimal bodily function. Reducing stress through relaxation techniques, such as meditation or yoga, may also improve sexual health. Importantly, discuss alcohol and tobacco use with your doctor; both can negatively affect sexual function.
Alternative Therapies
Some men find success with alternative therapies like pelvic floor physiotherapy. A physical therapist can guide you through exercises to strengthen and relax pelvic floor muscles, sometimes improving ejaculatory function. Additionally, counseling or therapy can be beneficial in addressing any underlying psychological factors contributing to ejaculatory issues. These factors may include anxiety, stress, or relationship problems. Open communication with your partner is critical for addressing relationship-related challenges.