Need the precise Chinese translation for Cialis? Use “西地那非” (Xīdì nàfēi) for the generic name Tadalafil. This ensures accurate communication with healthcare providers and pharmacists in China. Remember that pronunciation is key; mastering the tones is crucial for clear understanding.
For marketing materials, consider a more descriptive translation that conveys the drug’s function. Options include “他达拉非” (Tādá lāfēi), a slightly less formal version, or a phrase emphasizing its effects on erectile dysfunction, like “治疗勃起功能障碍的药物” (zhìliáo bóqǐ gōngnéng zàng’ài de yàowù), meaning “Medication for treating erectile dysfunction.” Consult a professional translator specializing in medical terminology for optimal results.
Caution: Directly translating brand names like “Cialis” may not be effective or legally sound in China. Always prioritize clear communication of the active ingredient and intended use. Using only the generic name avoids potential legal issues and ensures understanding.
Key Takeaway: Accurate translation is paramount. Prioritize using the generic name “西地那非” (Xīdì nàfēi) for medical contexts. For marketing, carefully select terms that clearly communicate the drug’s purpose without ambiguity.
- Cialis Chinese Translation: A Comprehensive Guide
- Understanding the Different Chinese Names for Cialis
- Accuracy of Cialis Translations in Chinese Online
- Verifying Translation Quality
- Risks of Inaccurate Translations
- Recommended Approach
- Using Reputable Sources
- Potential Risks of Using Unverified Chinese Translations for Cialis Information
- Finding Reliable Sources for Cialis Information in Mandarin
- Utilizing Reputable Online Pharmacies
- Leveraging Medical Professionals
- Navigating Online Forums and Communities
- Using Translation Tools Carefully
- Legal and Regulatory Considerations for Cialis in China
- Cultural Nuances in Communicating About Cialis in China
- Building Trust and Credibility
- Choosing the Right Channels
- Translating Cialis-Related Medical Terminology into Chinese
- Best Practices for Cialis Translation and Communication in a Chinese Context
Cialis Chinese Translation: A Comprehensive Guide
Use the official name provided by the manufacturer for accuracy and to avoid ambiguity. This ensures clear communication with healthcare professionals and pharmacists in China.
The most common and accepted translation is 西地那非 (Xī dì nà fēi). This is the transliteration of the generic name, sildenafil, the active ingredient in Cialis. However, this refers to the generic medication, not necessarily the branded Cialis.
- Consider the target audience: Are you translating for medical professionals, patients, or marketing materials? The appropriate level of detail and terminology will vary.
- Context matters: The translation should accurately reflect the specific use case. A medical pamphlet will differ significantly from an advertisement.
- Use professional translators: Engage a qualified translator with expertise in medical terminology and pharmaceutical advertising (if applicable) for best results. Relying on online tools alone is risky due to potential inaccuracies.
For branded Cialis, using the Pinyin transliteration of “Cialis” (希爱力 (Xī ài lì)) might be considered, though this is less common than using the generic name in medical contexts. Always check for official translations used by the pharmaceutical company operating in China.
- Verify accuracy: Always double-check the translation for accuracy and cultural appropriateness with a native Chinese speaker familiar with pharmaceutical terminology.
- Review legal implications: Ensure the translation complies with all relevant Chinese regulations concerning pharmaceutical advertising and labeling.
- Test the translation: Before widespread use, test the translated material with the target audience to ensure clear understanding.
Remember that even with careful translation, cultural nuances might require further adaptation for optimal comprehension and impact within the Chinese market.
Understanding the Different Chinese Names for Cialis
Cialis boasts several Chinese names, reflecting varying translation approaches and brand strategies. You’ll likely encounter 西地那非 (Xī dì nà fēi), a phonetic transcription of “tadalafil,” the generic name. This provides a clear scientific reference.
However, pharmaceutical companies often employ more descriptive brand names. One common alternative is a name emphasizing the drug’s function, like 勃起功能障碍药物 (bó qǐ gōng néng zàng ài yào wù) which translates to “erectile dysfunction medication”. This approach leverages understanding of the condition rather than the chemical name.
Important Note: Always verify the authenticity of Cialis from reputable sources to avoid counterfeit medications. Brand names vary regionally; what’s commonly used in one area may differ significantly in another. Consult a pharmacist or healthcare professional for clarification.
Finally, some informal names might circulate, but these should be approached with caution. Stick to names provided by licensed pharmacies or healthcare providers. Misidentification can lead to serious health problems.
Accuracy of Cialis Translations in Chinese Online
Finding reliable Cialis translations online requires careful scrutiny. Many websites offer translations, but accuracy varies significantly. Look for sites using professional translators specializing in medical terminology; this ensures correct interpretation of dosage, potential side effects, and contraindications. Generic translations often omit crucial details or use ambiguous phrasing, potentially causing harm.
Verifying Translation Quality
Check the translator’s credentials. Professional medical translators usually have certifications or affiliations with recognized medical institutions. Compare different translations; discrepancies highlight potential inaccuracies. If possible, consult a doctor or pharmacist fluent in both English and Chinese for validation.
Risks of Inaccurate Translations
Incorrect translations can lead to medication errors, missed warnings, and adverse health outcomes. For example, mistranslations about dosage could result in overdose or insufficient treatment. Misinterpretations of side effects can delay seeking necessary medical help. Always prioritize your health and seek professional guidance when dealing with prescription medications.
Recommended Approach
Consult your doctor or pharmacist before using any online resources for medication information. If you must use online translations, prioritize reputable sources that clearly state their translation process and credentials. Remember, your health is paramount.
Using Reputable Sources
Pharmaceutical company websites often provide accurate translations of medication information in multiple languages. Look for official sources linked to established healthcare providers and pharmaceutical manufacturers. Avoid relying on user-generated content or unofficial translations.
Potential Risks of Using Unverified Chinese Translations for Cialis Information
Misinterpretations of dosage and administration instructions can lead to ineffective treatment or adverse effects. Incorrect translations may result in taking too much or too little medication, potentially causing harm. Always consult a doctor or pharmacist for guidance on dosage.
Unreliable information about potential side effects is a major concern. An inaccurate translation might downplay or completely omit serious side effects, leaving users unaware of potential risks. Thoroughly research any medication before use, consulting reliable sources.
Counterfeit drug identification becomes significantly harder with unreliable translations. Identifying genuine Cialis packaging and verifying authenticity becomes challenging if you cannot accurately understand the Chinese text. Only purchase from reputable pharmacies and verified online vendors.
Inaccurate information about drug interactions poses a serious health risk. Misinterpreting drug interaction information can lead to dangerous combinations, resulting in unexpected and potentially severe side effects. Always disclose all medications you’re taking to your doctor.
Verify all information from independent and trustworthy sources before making any decisions about your health. Use reputable medical websites and consult healthcare professionals for accurate information regarding Cialis or any other medication.
Finding Reliable Sources for Cialis Information in Mandarin
Prioritize official websites of reputable pharmaceutical companies or government health organizations. Look for sites with a “.gov.cn” or “.org.cn” domain for increased credibility. These often provide accurate information about medications in simplified Chinese (简体中文).
Utilizing Reputable Online Pharmacies
If you need to purchase Cialis online, verify the pharmacy’s license and accreditation. Look for clear contact information, including a physical address, and customer reviews. Be wary of sites lacking this transparency.
Leveraging Medical Professionals
Consult a doctor or pharmacist who speaks Mandarin. They can offer personalized advice, address specific questions, and ensure safe medication practices.
Navigating Online Forums and Communities
While online forums can provide user experiences, treat information found there with caution. Verify information independently using trustworthy sources. Remember that personal experiences do not replace professional medical advice.
| Source Type | Reliability | Caveats |
|---|---|---|
| Government Health Websites (.gov.cn, .org.cn) | High | Information may be general, not personalized. |
| Licensed Online Pharmacies | Medium (Requires verification) | Risk of counterfeit medications; careful scrutiny needed. |
| Medical Professionals | High | Requires appointment and consultation fee. |
| Online Forums | Low | Unverified information; potential for bias and misinformation. |
Using Translation Tools Carefully
Employ reputable translation tools for navigating English-language medical information into Mandarin. However, always cross-reference with Mandarin-language sources for accuracy.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations for Cialis in China
Cialis, like all pharmaceuticals, requires stringent regulatory approval for sale in China. Importantly, you must obtain necessary licenses and permits from the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA). This involves a rigorous process, including clinical trials demonstrating safety and efficacy within the Chinese population.
Marketing and advertising regulations are particularly strict. Promotional materials must adhere to NMPA guidelines, accurately reflecting Cialis’s properties and potential side effects. Unapproved claims or misleading information can lead to severe penalties.
Intellectual property protection is crucial. Registering trademarks and patents protects your brand and prevents counterfeit products from entering the market. Aggressively combatting counterfeiting is vital due to the high prevalence of fake medications in China.
Distribution channels must comply with established pharmaceutical supply chain regulations. This includes maintaining proper storage and handling protocols to guarantee product integrity. Closely monitor the entire supply chain for potential breaches in regulatory compliance.
Finally, staying updated on evolving NMPA regulations is paramount. Regularly review the latest guidelines to ensure continuous compliance and avoid potential legal ramifications. Consulting with a legal expert specializing in Chinese pharmaceutical regulations is highly recommended.
Cultural Nuances in Communicating About Cialis in China
Directly address concerns about privacy and discretion. Chinese consumers highly value these aspects, especially regarding sensitive health topics. Use subtle, understated language in your marketing materials. Avoid overly explicit visuals or descriptions. Instead, focus on improving quality of life and enhancing relationships, subtly hinting at Cialis’s benefits without being graphic.
Building Trust and Credibility
Leverage endorsements from trusted Chinese medical professionals and celebrities. This helps build credibility and overcomes cultural hesitation surrounding Western pharmaceuticals. Focus on clinical data presented in a clear, concise, and easily understandable manner. Use visuals emphasizing natural elements and traditional Chinese medicine principles alongside scientific data to bridge the cultural gap. Emphasize long-term health benefits instead of solely focusing on immediate results. This resonates with the holistic healthcare approach prevalent in China.
Choosing the Right Channels
Utilize online channels frequented by the target demographic, focusing on reputable platforms with strong user trust. Consider collaborations with established Chinese e-commerce platforms and health websites to reach a wider audience. Respect Chinese cultural sensitivities in your advertising campaigns. Choose channels and approaches that align with Chinese cultural norms and preferences. Localize your messaging carefully for optimal impact, considering regional variations in language and cultural beliefs.
Translating Cialis-Related Medical Terminology into Chinese
Accurate translation requires careful consideration of nuanced meanings. Here’s a practical approach:
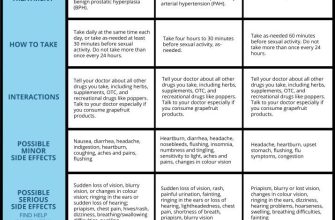
- Tadalafil: The generic name translates directly as 他达拉非 (tā dá lā fēi). This is the preferred term in medical contexts.
- Erectile Dysfunction (ED): Use 勃起功能障碍 (bó qǐ gōng néng zhàng’ài). Avoid colloquialisms for precision.
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH): Translate as 良性前列腺增生 (liáng xìng qián liè xiàn zēng shēng). This ensures clarity.
- Pulmonary Hypertension: This translates to 肺动脉高血压 (fèi dòng mài gāo xuèyā). Maintaining medical accuracy is vital.
When translating Cialis packaging or marketing materials, consider:
- Using simplified Chinese (简体中文) for mainland China and traditional Chinese (繁體中文) for Taiwan, Hong Kong, and Macau.
- Employing a professional medical translator familiar with pharmaceutical terminology and cultural sensitivities.
- Reviewing translations with medical professionals to ensure accuracy and clarity.
- Considering local regulations regarding pharmaceutical advertising.
For specific symptoms or conditions related to Cialis use, always prioritize consulting a medical dictionary and a professional translator specializing in medicine. Context is key; a direct, word-for-word translation might be misleading.
- Side Effects: Instead of a general translation, list each specific side effect and its Chinese equivalent. For example, “headache” translates to 头痛 (tóu tòng).
- Dosage and Administration: Be precise in translating dosage instructions, using the correct units and measurements (mg, tablets, etc.).
Remember that cultural considerations are paramount. Sensitivity and clarity are crucial for effective communication.
Best Practices for Cialis Translation and Communication in a Chinese Context
Prioritize accuracy above all else. Use professional medical translators familiar with pharmaceutical terminology and cultural nuances.
Consider regional variations. Mandarin differs significantly from Cantonese; target your translation to the specific dialect of your intended audience.
Employ culturally sensitive language. Avoid direct translations that might be misinterpreted. For example, subtle shifts in wording can greatly impact the perceived message regarding sexual health.
Address potential cultural sensitivities surrounding erectile dysfunction openly, yet respectfully. Maintain a tone that is informative and supportive, avoiding sensationalism or stigma.
Utilize clear and concise language. Avoid jargon and overly technical terms; explain complex information simply and directly.
Incorporate visual aids. Infographics or simple diagrams can improve understanding and engagement, particularly for complex medical information.
Test your materials thoroughly. Conduct pre-launch reviews with native Chinese speakers to identify and correct any ambiguities or cultural misunderstandings before release.
Choose the right channels. Understand your target demographic’s online habits and select suitable platforms for your campaign accordingly.
Monitor and adapt. Regularly review your campaign’s performance and make adjustments based on audience response and feedback.
Always comply with local regulations. Advertising pharmaceuticals requires adherence to strict guidelines and laws. Ensure your materials meet these requirements.